A virtual private network (VPN) extends a private network across a public network and enables users to send and receive data across shared or public networks as if their computing devices were directly connected to the private network.
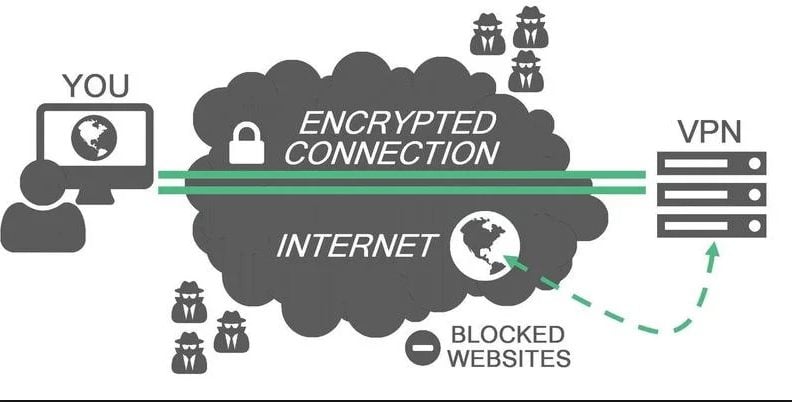
A VPN is a recent internet technology through which you can connect to the internet using a secure tunnel that keeps your information secure from others. It creates a tunnel between your computer and the internet connection that hides your real IP and computer details from the internet. It is the most useful tool to protect your online identity and information as well as your real location.
A VPN is very advantageous as it ensures a committed level of security and online privacy to the systems and devices you connect. It is highly useful when the current network infrastructure itself cannot support that level of security.
Let’s say, that when your device (PC or a Smartphone) is connected to a VPN app, the device works as if it exists on the same network as the VPN. All your traffic is moved over a secure and safe connection to the VPN app. Then that device will behave as if it is on that network, hence letting you securely get access to the resources of the local network. Regardless of the location you are sitting at, you would be able to access the internet as if you were sitting at the VPN server’s location. This becomes very useful for people who use public Wi-Fi.
A good VPN service would always ensure utter privacy and online security of its users. It is recommended to users go for the best VPN service whenever they have to buy one.
When you surf the web while connected with a VPN, your PC or smartphone will communicate with the internet via a secure and encrypted VPN connection. The VPN would then ultimately forward your request and bring the response from the web back again with a secure connection.
VPN services are very easy to use, and also considered as an effective internet tool that can be used for many purposes. With a VPN, you can perform many tasks even some of them you can’t imagine. You can connect to a server from a different location in the world, unblock the blocked websites, and apps, use different services that require unique IP addresses for multiple accounts. Moreover, you can obtain access to content on various devices, such as with a VPN for Firestick, where you can get ultimate access to your favorite shows and movies. Similarly, you can use a VPN with Roku, Kodi, Apple TV Box, and many other devices and enjoy lots of content immediately.

TYPES OF VPNs
There are 2 main types of VPNs i.e.
1. Remote-access VPNs
2. Site-to-Site VPNs
Remote Access VPN
Remote access VPN uses the public infrastructure to provide safe and private access to remote users in their network. This is extremely crucial for large government and private organizations.
It’s important when an employee connects to a public WiFi hotspot and uses any of the internet resources for sending an email that is confidential to that organization. A VPN client on the user’s mobile, MacBook, smartphone or any device connects to the VPN gateway on the organization’s network. This gateway needs the device to ensure its identity. Then it will make a network connection back to the device which will allow it to access network resources that include intranets, file servers, and printers just as they all were on the same network.
Site-to-Site VPN
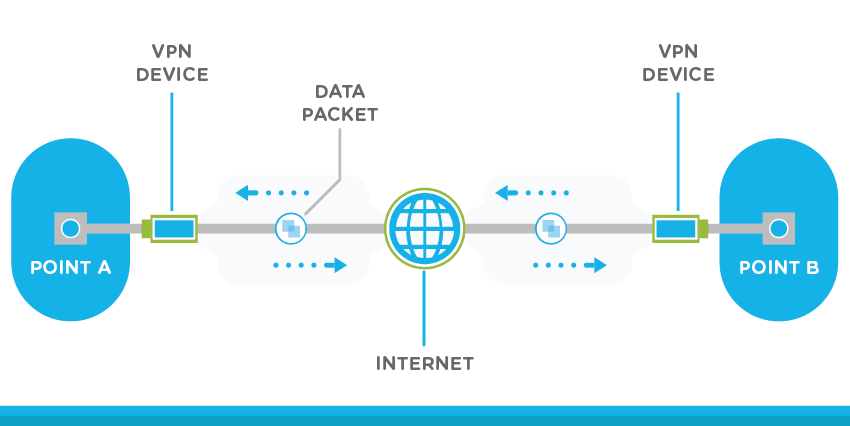
A site-to-site VPN makes use of a gateway device for connecting to the whole network at one location to a network available at another location. Most of the site-to-site VPNs use IPsec to connect to the internet. Instead of using a public internet resource, it is normal to use carrier multi-protocol label switching (MPLS) clouds as the major transport for site-to-site VPNs.
VPNs are usually connected between a specific computer to another computer, and mostly, their servers are placed in all different data centers. However, nowadays the latest technology of hybrid-access situations have transformed the gateway of the VPN in the cloud, usually with a secure link from the cloud service provider into its internal network.